- Product Description
- Product Highlights
- Contact Information
- New Features
- Defects Fixed
- Documentation
- Contents of Release
- Platforms Supported
Product Description
CUBIT™ is a full-featured software toolkit for robust generation of two- and three-dimensional finite element meshes (grids) and geometry preparation. Its main goal is to reduce the time to generate meshes, particularly large hex meshes of complicated, interlocking assemblies.
Product Highlights
Meshing: CUBIT™ is a solid-modeler based preprocessor that meshes volumes and surfaces for finite element analysis. Mesh generation algorithms include quadrilateral and triangular paving, 2D and 3D mapping, hex sweeping and multi-sweeping, tet meshing, and various special purpose primitives. CUBIT™ contains many algorithms for controlling and automating much of the meshing process, such as automatic scheme selection, interval matching, sweep grouping and sweep verification, and also includes state-of-the-art smoothing algorithms.
Geometry Preparation: One of CUBIT™’s strengths is its ability to import and mesh geometry from a variety of CAD packages. CUBIT™ currently integrates the ACIS and Catia geometry kernels directly within its code base, allowing direct manipulation of the native CAD geometry format within CUBIT™. This reduces the errors and anomalies so often associated with geometry translation. CGM (Common Geometry Module) also boasts a facet-based geometry kernel developed at Sandia that can be used for remeshing or editing old mesh files or models defined by triangle facets. In addition, CUBIT™ has developed a comprehensive virtual geometry capability that permits local composites and partitions to geometry without modifying the underlying native geometry representation. The user can choose to ignore, clean-up or add features to the model allowing greater flexibility to meshing algorithms to generate better quality elements.
CUBIT™ Environment: CUBIT™ has developed both a convenient command line interface with an extensive command language as well as a polished graphical user interface environment. The GUI is based upon the cross-platform standard Qt, which allows the same look and feel on all supported platforms. Also included is a graphical environment based upon the VTK graphics standard which has been optimized for display and manipulation of finite element data and geometry. Fast, interactive manipulation of the model is a tremendous advantage for models with thousands of parts or millions of elements.
For more information on CUBIT™, including licensing arrangements and terms see the CUBIT™ website https://cubit.sandia.gov
New Features in CUBIT™ 15.9
Index of New Features
- Enhanced reduce panel
- Enhanced geometry power tool
- New breadcrumb navigation for command panels
- New uniform mesh refinement panel
- Enhanced pick widget context menu
- Minimum edge length
- Sizing on discrete curves
- Clean discrete mesh command
- Sculpt enhancements
- Paving with small features
- Restricted stitch command
- New reduce spring command
- Regularize command keep option
- Imprint with tolerance
- Include parsing
- New GDF exporter
- New OBJ importer
- Importing with block names
- Exodus ID map control
- Parallel consistency in UMR
- New CubitInterface functions
Graphical User Interface
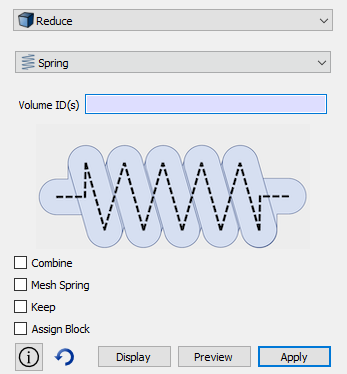
Enhanced reduce panel
The reduce command panel now has options for reducing springs.
Enhanced geometry power tool
The geometry power tool now shows solutions for bolt and spring categories.
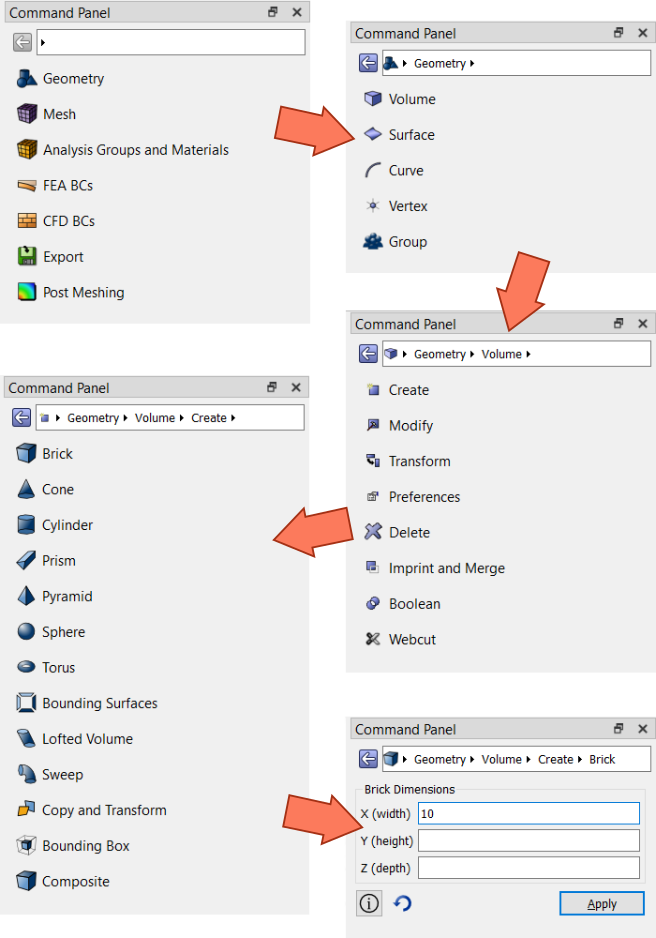
New breadcrumb navigation for command panels
A new type of navigation has been added to the command panels. In order to save space for the command panel widgets, an interactive breadcrumb trail has been added to the top of the panels to replace the rows of buttons. There is a setting to change back to the button rows if desired. The new breadcrumb trail shows where you are in the command panel hierarchy. The panel below the trail shows either a command panel or a list of possible commands or categories. The following figure shows how to navigate to the “create brick” command panel in “classic” layout.
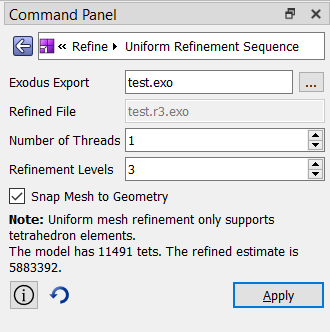
New uniform mesh refinement panel
The UMR (Uniform Mesh Refinement) tool now has a command panel in CUBIT™. It sets up a run, or a sequence of runs, using the current meshed model. The UMR tool only supports tetrahedral elements at this time.
Enhanced pick widget context menu
The GUI pick widget, which is used to select entities for command panels, has been improved to better support standard cut, copy, and paste. When multiple entities are selected, the IDs displayed are compressed using the “to” syntax that can be used when typing the command in manually.
Meshing
Minimum edge length
A new command was added to set the minimum edge length for tet-meshing. Setting the minimum edge length prevents other sizing parameters, such as curvature, from producing mesh edges that are too small. However, smaller mesh edges will still be produced if there are any geometry edges smaller than the given size.
[set] tetmesher HPC minimum edge length [<value>]
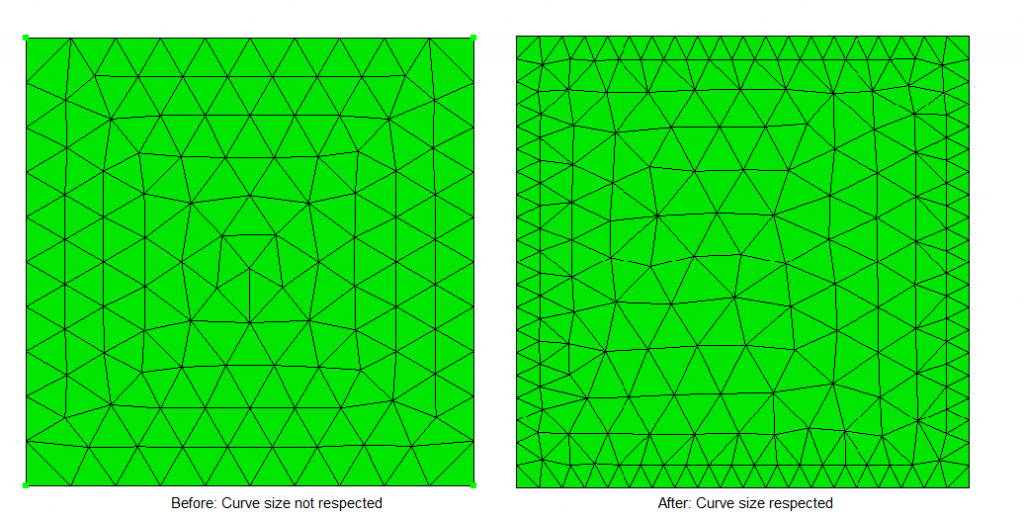
Sizing on discrete curves
Mesh sizing on curves of a discrete surface are now respected during triangle meshing.
Clean discrete mesh command
An option was added to clean the discrete geometry prior to tri-meshing. This step remeshes the underlying triangles of the discrete geometry surface to improve the representation prior to meshing with user defined sizes. This is useful if the underlying facets representing the discrete surface are not an optimal representation of the surface.
[Set] Trimesher Clean Discrete Mesh {on|OFF}
Sculpt enhancements
Two new adapt_type options have been added: resample and material. With the resample option, the input volume fraction data from microstructure file formats (input_micro, input_cart_exo and input_spn) is down sampled, averaging volume fraction data across multiple cells according to the adapt_levels set. With the material option, refinement is done in cells where the predominant volume fraction is a user specified material ID. To specify that material ID, use the new “adapt_material” option.
A new “geometry_and_blocks” option has been added to “input_mesh_material“. with this option, the block IDs in the final mesh come from the input genesis blocks and materials from the diatom/STL file.
Two new options have been added to use with the free_surface_sideset option. The first is the new sheet wear method. This option wears a swept input mesh in layers. The second is the crack_min_element_thickness, which is used with the sheet wear method. It defines the minimum allowed thickness of the elements resolving the side of a crack.
The new input_stitch file format allows Sculpt to read a stitch file. Stitch is a new I/O system that has been added to Sandia’s SPPARKS (Stochastic Parallel PARticle Kinetic Simulator) tool. See dump stitch and set stitch for more details. See also options stitch_timestep, stitch_timestep_id, stitch_field, and stitch_info that support the new input_stitch capability.
Paving with small features
The paving scheme is more robust in cases where mesh size approaches feature size, especially at holes. Improvements have corrected the algorithm from meshing over small holes. Increased element quality is also another benefit.
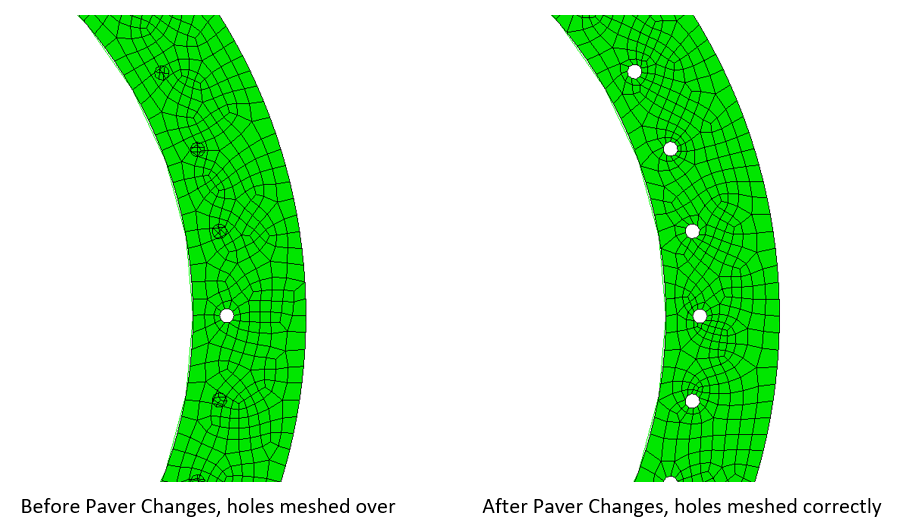
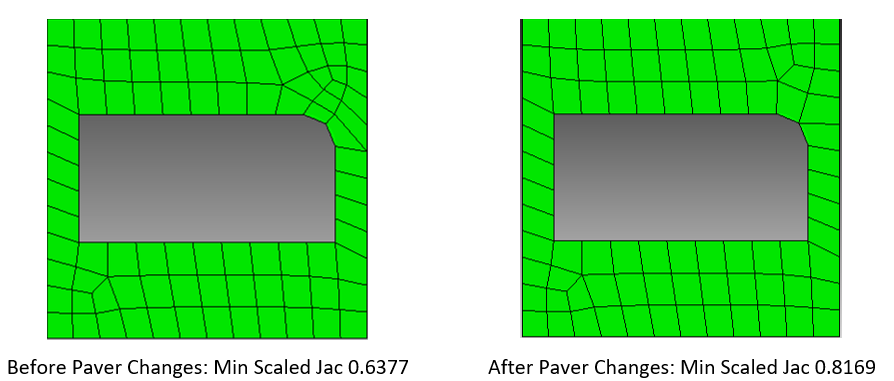
Geometry
Restricted stitch command
A ‘restricted’ parameter has been added to the stitch command. It allows stitching to operate in ‘restricted’ mode, where only the boundary edges of the sheet bodies or volumes participate in the stitch operation. This improves performance for large models.
Stitch {body <ids>|volume <ids>} [tolerance <value>] [no_simplify] [no_tighten_gaps] [restricted]
New reduce spring command
The new reduce spring command has the ability to reduce a 3D spring volume to a series of curves.
Reduce {volume <ids>} spring [combine] [mesh [size {<value>}]] [keep] [block_id {<value>|Default}] [increment_block_id] [block_name {<string>|Default}] [preview]
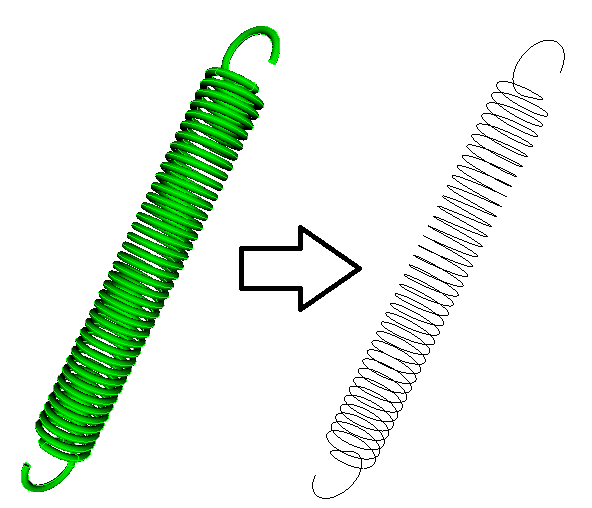
Regularize command keep option
The regularize command now has a keep option that allows the specified curves and vertices to survive the operation.
Regularize {body <ids>|group <ids>|volume <ids>| surface <ids>|curve <ids>|vertex <ids>} [keep {curve <ids>|vertex <ids>}]
Imprint with tolerance
A new optional tolerance parameter has been added to the volume/vertex imprint command.
Imprint {Volume|Body} <range> [with] Vertex <range> [keep] [tolerance <value>]
Include parsing
New options can now be used with the include parsing keyword: similar, cavity, hole, blend_chain, chamfer_chain, continuous, and nearby. The parser compares the specified entities and includes additional entities that match the criteria. For example:
draw volume 1 include nearby
select surface 10 include hole
remove surface 20 include blend_chain
Machine Learning
New “thin” category
A new category has been added to the machine learning classification categories: thin. This new category can be used to identify thin regions of the model.
New training commands
Several new commands have been added to support machine learning categorization.
Classify {volume <ids>} [confidence][features [importance]]
This computes the current classification prediction. The ‘confidence’ option displays prediction confidence for each category. The ‘features’ and ‘importance’ options list internal values used for machine learning training along with their relative importance to classification.
Classify {volume <ids>} “<string>” [export_acis]
This command adds volume(s) to the user training data with the specified string as its category. The ‘export_acis’ option exports one ACIS file per specified volume into the user training directory.
Reclassify {volume <ids>} “<string>”
This command removes volume(s) from their existing classification and reclassifies them to the category specified by ‘string’.
Classify List
This command invokes training with all current training data. It lists accuracy and support for each category.
Classify Reset [“<string>”]
This command removes all user training data with the category specified by ‘string’. If no ‘string’ is specified, all user training data will be removed.
Categories in extended parsing
Machine learning categories can now be used in extended parsing. The ‘with “category” ‘ syntax can be used to find entities of a category. For example:
draw volume with category “spring”
Note: this will be slow if many volumes exist since machine learning will process all volumes to determine which ones are springs.
File I/O, UMR, etc.
New GDF exporter
A new export command has been added to support the GDF (Geographic Data Files) format. The command syntax is:
Export GDF '<filename>' {<entity_list> | block <range>} [ulen <value=1.0>] [gravity <value=9.80665>] [isx <value=0> ] [isy <value=0>] [overwrite]
New OBJ importer
Cubit is now able to import OBJ files that contain tessellation of polygonal faces.
Import Obj <string> [FEATURE_ANGLE <value>] [SURFACE_FEATURE_ANGLE <value>] [make_elements]
Importing with block names
The import mesh and import mesh geometry commands have a new “block_name” option. This option allows the user to import only the mesh from the named blocks.
Exodus ID map control
The export exodus command now has an option to control whether or not the ID map is written to the exodus file. By default, the map is written out. Add the “no_ids” option to the command to prevent the map from being written.
Export [Genesis | Mesh] '<filename>' [Dimension {2|3}] [Block <id_list>] [Qualityfile] [no_ids] [Overwrite] [XML ['<xml_filename>']]
Parallel consistency in UMR
UMR (Uniform Mesh Refinement) has been improved to generate a consistent refined mesh.
New CubitInterface functions
CubitInterface is CUBIT™’s python module that provides extensive capability for querying and modifying data in CUBIT™. The following functions were added to CubitInterface for version 15.9.
| Function Name | Description |
| get_bolt_diameter | Gets diameter of bolt shank |
| get_bolt_axis | Gets axis vector of bolt |
| get_num_volume_shells | Gets the number of shells in a volume |
| get_ML_classification_models | Gets the available classification ML model names |
| get_ML_regression_models | Gets the available regression ML model names |
| get_ML_model_ID | Gets a unique ID for the given operation/model name |
| get_ML_model_name | Gets the name for the given operation/model ID |
| get_similar_curves | Gets curves with the same length |
| get_similar_surfaces | Gets surfaces with the same area and number of curves |
| get_similar_volumes | Gets volumes with the same volume and number of faces |
| get_similar_curves | Added tolerance option to this existing command |
Defects Fixed in CUBIT™ 15.9
The following items are the user-reported bugs fixed since the last release of CUBIT™. For more information contact Roshan Quadros (wrquadr@sandia.gov).
| Ref # | Description |
| MESH-520 | Open exodus file in lite or no_geom mode |
| MESH-3930 | Fix for bug in sculpt option ‘mesh_void’ |
| MESH-4337 | Cubit 15.5 and Python 3 on Mac startup issue |
| MESH-4495 | Add python “group_names_ids” to documentation |
| MESH-4503 | Launch Error with 15.5 on Mac OS 10.14.6 |
| MESH-4562 | Add support for functional selection set even with graphics disabled |
| MESH-4751 | ‘Unite volume include_mesh’ changes owned entities from volumes to hexes |
| MESH-4773 | HO element type not kept during copy |
| MESH-5026 | ‘set copy_block_on_geometry_copy on’ behavior incorrect |
| MESH-5107 | Fix for hang in spider command |
| MESH-5251 | Coloring spider elements by block |
| MESH-5290 | Fix difference between “cubit -h” and “cubit -help” |
| MESH-5319 | Add exodus export transformation to GUI |
| MESH-5346 | Losing printed strings with python 3 |
| MESH-5384 | If no cubit.init set Cubit should have a fall back |
| MESH-5385 | Open graphics window from python script |
| MESH-5392 | Add PyCubed_User_Documentation to site-packages directory |
| MESH-5478 | Added option to remove explicit node map on output |
| MESH-5479 | Crash while meshing or interacting with graphics window |
| MESH-5498 | Fix for cubit-python enhancements broken in 15.8, alpha and beta |
| MESH-5500 | Switch between internal and external python scripts – via GUI switch |
| MESH-5504 | Easier hardcopy in both interactive and from workflows |
| MESH-5506 | Added unique_genesis_ids as a menu option |
| MESH-5507 | Open file in cubit – make the list of options the same as that from the import command |
| MESH-5508 | Click on a volume and have the block ID highlight if the volume is part of a block |
| MESH-5523 | No Cubit after module load sierra |
| MESH-5538 | Ability to import named block in import mesh command |
| MESH-5564 | Fix for crash when collapsing selected tet |
| MESH-5565 | Performance issue with right click context menu |
| MESH-5595 | Duplicate IDs in model tree – refresh event needed |
| MESH-5599 | ‘Select similar’ feature requests |
| MESH-5609 | Put Coreform collapsing command button code into Cubit |
| MESH-5614 | Fix ‘find curve overlap’ slowdown |
| MESH-5629 | Nodesets getting returned with sidesets |
| MESH-5632 | Keyword names when importing SAT files |
| MESH-5662 | Bug fixes in ‘reduce bolt’ functionality |
| MESH-5666 | Python’s “quit()” function in the “clarox” executable causes an error message |
| MESH-5697 | False positive bad Euler number, invalid mesh |
| MESH-5716 | Sideset and nodeset character limit in GUI |
*The defects listed above are only those user-reported issues deemed “critical” or “blocker”. For information on other known defects contact Roshan Quadros.
Documentation Updates
The CUBIT™ 15.9 online documentation may be found here. A PDF version is also available for download. The CUBIT™ GUI installation also includes the full user documentation included with the program. The user’s manual may be accessed from the Help menu.
CUBIT™ 15.9 Contents of Release
CUBIT™ Program: The installation package includes executables and libraries, packaged in tar.gz files for Linux machines. For Windows, the package is in a self-installing executable, and for Mac OS X a .dmg file is provided. Both a command line and GUI version of CUBIT™ are included with the installation package for all platforms.
Documentation: Linux, Windows and Mac versions include full online documentation. Windows also includes .chm (Windows Help File), of the complete documentation that can be run separately from CUBIT™.
Platforms Supported
CUBIT™ 15.9 supports the following Platforms:
- Linux RedHat Enterprise 7 and 8
- Windows 10, 8 and 7
- macOS 10.11+
Non-Sandia Users
CUBIT™ is freely available for United States government use. For more information on licensing CUBIT™, including academic, commercial, and all other use, go to our licensing page. For current CUBIT™ users, CUBIT™ 15.9 may be downloaded from the CUBIT™ download page.
Sandia Personnel Only
CUBIT™ 15.9 may be downloaded from the CUBIT™ download page.
Windows
Download a Windows installation file and double-click to install.
MAC OS X
Download a Mac OS X disk image file. After the disk image is opened, click and drag the CUBIT™ folder to /Applications.
LINUX LANS
Check with your local LAN administrator for instructions on how to access CUBIT™ on your local LAN. In most cases typing one of the following commands at the UNIX prompt should allow you to execute CUBIT™. In some cases, the full path will need to be specified:
/projects/cubit/<cubit_command>
| cubit | The latest released version (15.9) of CUBIT™ deployed to the LAN. |
| cubit -nogui | The latest released version (15.9) with just the Command Line and graphics window |
| cubit -nogui -nographics | The latest released version (15.9) with just the Command Line |
| cubit-15.9 | Version 15.9 with GUI |
| cubit-beta | The latest beta version still in development |
Contact Information
CUBIT™ Help
For general technical questions including download, installation and CUBIT™ technical assistance.
CUBIT™ Licensing and Passwords
Email: cubit-req@sandia.gov
CUBIT™ Support Lead
Trevor Hensley
Phone: 505-284-7756
Email: cubit-help@sandia.gov
CUBIT™ Project Lead
Roshan Quadros
Sandia National Laboratories
Computational Simulation Infrastructure (org. 1543)
Phone: 505-844-0408
Email: wrquadr@sandia.gov
Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-mission laboratory managed and operated by National Technology & Engineering Solutions of Sandia, LLC., a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International, Inc., for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-NA0003525. SAND2017-6996 W
