- Product Description
- Product Highlights
- New Features
- Defects Fixed
- Documentation
- Contents of Release
- Platforms Supported
- Contact Information
Product Description
Cubit® is a full-featured software toolkit for robust generation of two- and three-dimensional finite element meshes (grids) and geometry preparation. Its main goal is to reduce the time to generate meshes, particularly large hex meshes of complicated, interlocking assemblies.
Product Highlights
Meshing: Cubit® is a solid-modeler based preprocessor that meshes volumes and surfaces for finite element analysis. Mesh generation algorithms include quadrilateral and triangular paving, 2D and 3D mapping, hex sweeping and multi-sweeping, tet meshing, and various special purpose primitives. Cubit® contains many algorithms for controlling and automating much of the meshing process, such as automatic scheme selection, interval matching, sweep grouping and sweep verification, and also includes state-of-the-art smoothing algorithms.
Geometry Preparation: One of Cubit®’s strengths is its ability to import and mesh geometry from a variety of CAD packages. Cubit® currently integrates the ACIS and Catia geometry kernels directly within its code base, allowing direct manipulation of the native CAD geometry format within Cubit®. This reduces the errors and anomalies so often associated with geometry translation. CGM (Common Geometry Module) also boasts a facet-based geometry kernel developed at Sandia that can be used for remeshing or editing old mesh files or models defined by triangle facets. In addition, Cubit® has developed a comprehensive virtual geometry capability that permits local composites and partitions to geometry without modifying the underlying native geometry representation. The user can choose to ignore, clean-up or add features to the model allowing greater flexibility to meshing algorithms to generate better quality elements.
Cubit® Environment: Cubit® has developed both a convenient command line interface with an extensive command language as well as a polished graphical user interface environment. The GUI is based upon the cross-platform standard Qt, which allows the same look and feel on all supported platforms. Also included is a graphical environment based upon the VTK graphics standard which has been optimized for display and manipulation of finite element data and geometry. Fast, interactive manipulation of the model is a tremendous advantage for models with thousands of parts or millions of elements.
For more information on Cubit®, including licensing arrangements and terms see the Cubit® website.
New Features in Cubit® 17.06
Index of New Features
- Improved robustness of triangle and tet meshing
- Increased accuracy and precision when computing mesh quality metrics
- New mesh quality metrics for higher order elements
- New cohesive element generation for crack propagation and cohesive interfaces
- New skew control option for curve skinning
- Dark Mode Support
- PNG default for shortcut when saving image file of graphics view
- Journal editor enhancements
- New support for additional ABAQUS cards when importing files
- New 64 bit ID support in Exodus files
- New features for graph neural network models
- Faster feature compute times
- Support for user-defined mesh configuration settings
- New set error on/off for filtering messages
- Updated Python 3.12 version included in distribution
- Improved documentation for Python API
- More robust cavity selection
Meshing
Improved robustness of triangle and tet meshing
Triangle and Tet meshing has been improved for better stability and mesh quality. This can be particularly noticeable on models with composite surfaces. While most models saw normal meshing operation, some did not. Below is an example of a case that was corrected.
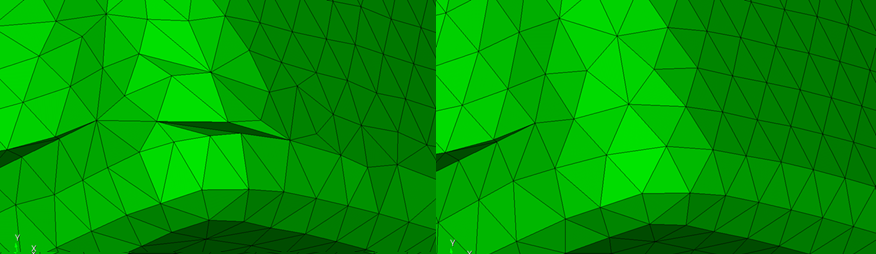
For more information see: Trimesh
Increased accuracy and precision when computing mesh quality metrics
Mesh quality metrics have improved accuracy and precision, specifically those metrics with normalized values. For example, an extremely tiny tet element could see a more accurate scaled Jacobian metric.
For more information see: Mesh Quality Assessment
New mesh quality metrics for higher order elements
Jacobian and scaled Jacobian metrics are now implemented for Tetra10 and Tri6 higher order elements. These metrics now have the ability to detect poorly shaped elements due to poor placement of mid-edge nodes.
For more information see: Higher Order Metrics
New cohesive element generation for crack propagation and cohesive interfaces
A new method is introduced to support creation of cohesive elements. This is useful for crack modeling and cohesive interface modeling. The new create cohesive element block <value> surface <ids> command will unmerge the given surfaces, and insert cohesive elements in the newly unmerged region. This modeling technique can also be combined with pre-cracking, where a portion of the crack is already separated.
For more information see: Creating Cohesive Elements
Geometry
New skew control option for curve skinning
A new pair tolerance <value> option is available for the create surface skin curve command to control potential skew. Vertices in the given curves are paired within tolerance, and if a pair is not found, a new vertex is introduced. This behavior is now the default behavior when giving the skin option for the reduce surface slot command.
For more information see: Create Surface
Graphical User Interface
Dark Mode Support
Support for dark mode has been improved by fixing highlight colors, and adding a dark mode icon pack so that icons and text are more clearly visisble. In addition, some of the new icons have been tweaked to better match the original designs so they are more recognizable to long term users.
PNG default for shortcut when saving image file of graphics view
When using the control-h key to save a snapshot of the graphics view, a .png is now created, instead of .jpg.
Journal editor enhancements
The journal editor now has new F5 and Control-F5 option for playing the whole script or the selection portion of the script. Also, the font has been corrected to use a fixed width font, or follow the user selected font.
For more information see: Journal File Editor
Input/Output
New support for additional ABAQUS cards when importing files
ABAQUS cards MASS and CONNECTOR are now supported. Also, part transformation issues in some models has been corrected. Grouping of nodes and elements when importing a file has been improved and made consistent with respect to the multiple ways of specifying groups.
For more information see: Exporting ABAQUS
New 64 bit ID support in Exodus files
Cubit® is now able to write Exodus files with 64 bit ids. The user interface is updated to provide this option and a new command set exodus 64bit {on|off} is available for scripts.
For more information see: Exporting an Exodus II File
Machine Learning
New features for graph neural network models
Cubit® now supports five new feature strategies for graph neural networks: vertex-nodes, curve-nodes, surface-nodes, vertex-curve-edges, and vertex-surface-edges. These strategies are designed around a graph representation of BRep topologies in terms of vertex, curve, and surface nodes connected by edges between vertex-curve and vertex-surface pairs. These features can be accessed via the get_ML_features function in the Cubit® Python API.
For more information see: Cubit® Python API
Faster feature compute times
We removed proximity-based features from our feature sets due to unacceptably long compute times. These features were designed to identify neighboring entities positioned close to each other in Cartesian space; however, the polynomial runtimes required to identify these entities cannot be justified by their relatively small improvement in machine learning prediction accuracy.
Support for user-defined mesh configuration settings
Cubit® now supports a set of user-defined mesh configuration settings (geometry sizing and regularization) directly in the feature sets for our mesh quality prediction models. This empowers the user to generate machine learning models for the specific mesh configurations that best fit their use case. Support for more configurations will be added in future releases.
Miscellaneous
New set error on/off for filtering messages
It is now possible to disable printing of error messages, similar to how it is possible to disable warning and information messages. This can be done using the set error {on|off} command.
For more information see: Message Output Settings
Updated Python 3.12 version included in distribution
Cubit® now includes Python 3.12 which is used when running scripts within Cubit.
Other versions of Python 3 continue to be compatible when Cubit® is imported into an externally executed Python script.
Improved documentation for Python API
The Python API documentation has been enhanced to provide more description on usage, and more examples.
For more information see: Cubit® Python API
More robust cavity selection
The existing surface cavity selection tools have been enhanced with a more robust cavity identification algorithm that no longer flags spherical protrusions or near 180° blend surfaces as cavities.
For more information see: Right Click Commands
User Requests and Bug Fixes in Cubit® 17.06
- MESH-8776 Fix subtract icon
- MESH-8743 Fix higher-order node problem with loosely associated mesh (from collapses)
- MESH-8780 Cubit 17.04 will not launch on CEE LAN because of venv setup
- MESH-8808 Cubit 17.04 on Ubuntu 24.02.2 LTS
- MESH-8784 Volume > Subtract image needs to be a little smaller
- MESH-8781 Background color in Journal Editor in Dark Mode
- MESH-8765 Tet Mesh Gradation
- MESH-8864 python help doesn’t work in 17.04
- MESH-8853 tab not working to select stuff
- MESH-8770 GUI dropdown menu not working in Cubit 16.18.1 on macOS 15.4
- MESH-5663 push a Verdict update to github
- MESH-8489 empty nodesets and sideset imported
- MESH-7250 crash in meshing massive composite surface
- MESH-3646 paver failure example
- MESH-1402 Stylesheet Editor
- MESH-8275 cubit app icons
- MESH-8893 large increase in Cubit mesh times
- MESH-8837 Swapping normals causes meshing to crash.
- MESH-8988 sgm step export corrupts three volumes model
- MESH-8887 libGL error for cubit
- MESH-8790 get_center_radius not returning arc center correctly
- MESH-9017 Cubit Python API Surface.ordered_loop()
- MESH-8180 Clean up Python API documentation
- MESH-9047 Extract Parameters of a Spline
- MESH-9056 faceting issue affecting NGS
- MESH-8782 SVG icons need to change in Dark Mode
- MESH-8835 Cubit imports Abaqus INP incorrectly
- MESH-8820 Cubit improperly selects faces/tris in sidesets created using patch center
- MESH-6519 Mac downloads of Cubit® not opening
- MESH-5926 Curves at Sharp vertices
- MESH-3720 automatic fallback to mesa/libGL.so.1 when using python
- MESH-3647 Resize Command Panel in GUI
- MESH-2521 meshing with sweep
- MESH-366 Cubit to output block masses after access to density
- MESH-8842 Upgrade to macOS Sequoia 15.4 I/O loss of functionality
- MESH-8788 Increase Fontsize of Command Line
- MESH-7609 Icon Sizing for Large Monitors
- MESH-9105 Documentation Link Not Working
- MESH-8892 Spyder IDE issue
- MESH-8761 trimesh crash
- MESH-8320 crash trimeshing composite
- MESH-8787 Cubit trimesh Crash
- MESH-8894 simple trimesh crash
- MESH-8994 simplest failure of meshing composite surfaces
- MESH-9052 Maximum entity name size limit when importing Abaqus
- MESH-8284 Support CIRCLE element in Cubit
- MESH-1269 Mesh overlap detection – mesh to mesh, or ACIS to mesh
- MESH-995 save a measured distance output for later usage
- MESH-632 Does cubit output the area moment of inertia?
- MESH-9104 PickWidget Palette unreadable in dark mode
- MESH-8789 trimeshing hangs Cubit
- MESH-8766 trimesh composite crash
- MESH-1509 Model tree incorrectly reporting 0 elements for Sheet Bodies
- MESH-9134 Redesign icons that are less recognizable
- MESH-9074 node constraint off not in documentation
- MESH-9065 Play Journal file Icon not working on 17.04
- MESH-9064 Regularize curve causes a crash
- MESH-5431 Trimeshing a composite containing a partition
- MESH-8321 triangle meshing problems
- MESH-8711 crash in tri/tet meshing
- MESH-1900 Trimeshing a composite containing a partition
- MESH-8984 Major slowdown in triangle refinement
- MESH-9015 Performance hit adding higher order nodes
- MESH-8177 sgm_viewer on RHEL8 – error while loading shared libraries: libpng15.so.15
- MESH-7467 holes not completely identified
- MESH-7472 python loop issue, cut & paste script works, but running it doesn’t
- MESH-7453 gui gives incorrect command for sweep surface with target plane
- MESH-7615 Yellow current line in Journal Editor conflicts with color in Mac night mode
- MESH-8792 cubit hanging when trimeshing
- MESH-8326 trimeshing generating sliver tris
- MESH-4963 Documentation – Cubit from console on Windows
- MESH-4791 Add user-dev python scripts to Cubit installation
- MESH-8748 C++ commands look like python in documentation?
- MESH-8490 bug in meshgems 2.15 with quadratic meshing
- MESH-8344 meshgems option not working in trimesh command
- MESH-8885 step file doesn’t loading in python on Windows
- MESH-8708 mid edge nodes snapped incorrectly to surface
- MESH-7598 Cubit Tet10 Graphics Bug
- MESH-3230 higher-order elements causing double resolution
- MESH-8554 split curve close_to vertex is broken
- MESH-8241 Python Switch In Journal Script
- MESH-7758 scheme ‘sphere’ not restoring correctly
- MESH-744 Inverted pyramids
- MESH-9079 Small change required in sierra export
- MESH-8575 get_surface_cone_collections() crashes
- MESH-8879 “joint node spider surface” does not spider mid-side nodes
- MESH-9146 scheme map choosing wrong vertex
- MESH-9095 Grouping By Blocks
- MESH-7122 Cubit GUI incorrectly sorting nodes in list
- MESH-8204 spider to default to bar element
- MESH-7311 Diagnose Geometry tab doesn’t consider sheet bodies
- MESH-7307 webcut with general plane case not working
- MESH-7272 Unexpected behavior with rebar command
- MESH-7130 right-click ‘select chamfer chains’ taking too long
Documentation Updates
The Cubit® 17.06 online documentation may be found here. A PDF version is also available for download. The Cubit® GUI installation also includes the full user documentation included with the program. The user’s manual may be accessed from the Help menu.
Cubit® 17.06 Contents of Release
Cubit® Program: The installation package includes executables and libraries, packaged in tar.gz files for Linux machines and a self-installing executable for Windows. Both a command line and GUI version of Cubit® are included with the installation package for all platforms.
Documentation: Both Linux and Windows versions of Cubit® include full online documentation.
Platforms Supported
Cubit® 17.06 supports the following Platforms:
- Linux RedHat Enterprise 8
- Windows 11
Non-Sandia Users
Cubit® is freely available for United States government use. For more information on licensing Cubit®, including academic, commercial, and all other use, go to our licensing page.
Sandia Personnel Only
Cubit® 17.06 may be downloaded from the Cubit® download page.
Windows
Download a Windows installation file and double-click to install.
Linux Desktop
Decompress and extract the .tar.gz archive, then run the ‘cubit’ script in the Cubit-17.06 directory
Linux LANs
Check with your local LAN administrator for instructions on how to access Cubit® on your local LAN. In most cases typing one of the following commands at the UNIX prompt should allow you to run Cubit®. In some cases, the full path will need to be specified: /projects/cubit/<cubit_command>
| cubit | The latest released version (17.06) of Cubit® deployed to the LAN. |
| cubit -nogui | The latest released version (17.06) with just the Command Line and graphics window |
| cubit -nogui -nographics | The latest released version (17.06) with just the Command Line |
| cubit-17.06 | Version 17.06 with GUI |
| cubit-beta | The latest beta version still in development |
Contact Information
Cubit® Help
For general technical questions including download, installation and Cubit® technical assistance.
Cubit® Licensing and Passwords
Email: asc-approvals@sandia.gov
Cubit® Support Lead
Trevor Hensley
Phone: 505-844-3304
Email: cubit-help@sandia.gov
Cubit® Project Lead
Ryan Viertel
Email: rvierte@sandia.gov
