Cubit 16.04 User Documentation
Type "cubit" from a UNIX prompt or select cubit from the start menu if you are running on a PC with Windows. The CUBIT Application Window will appear as illustrated below:

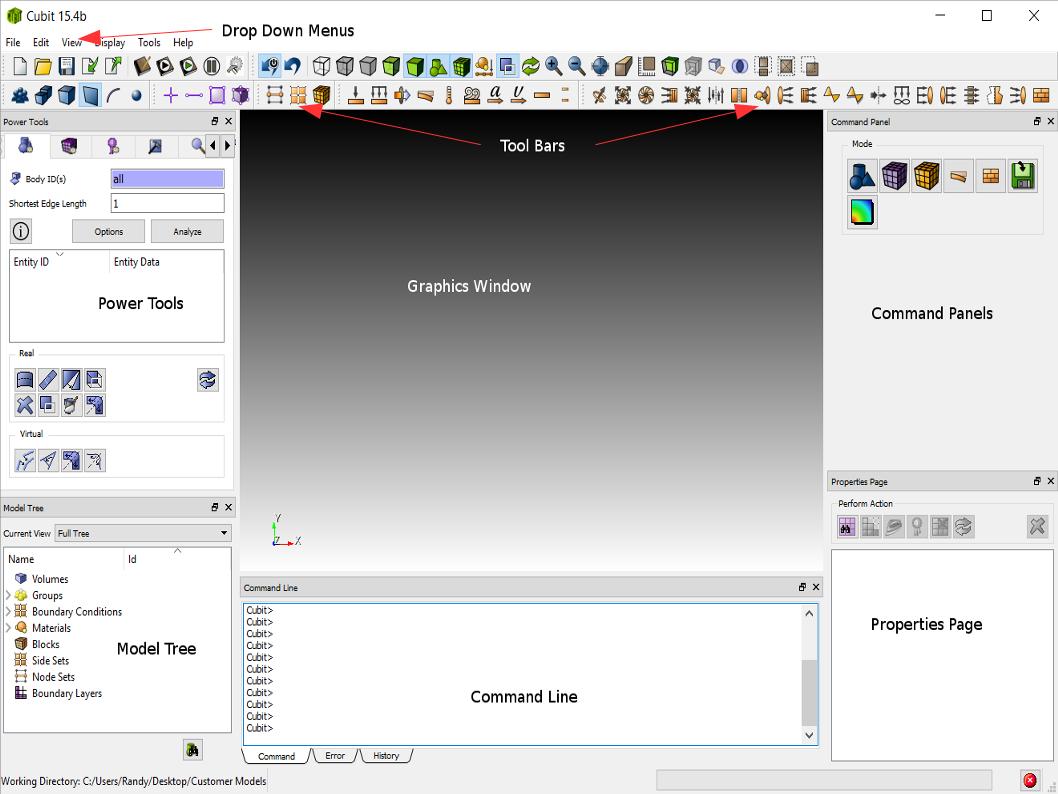
CUBIT Application Window
The use of each window in the CUBIT program is described briefly below
| Graphics Window | The current model will be displayed here. Zooming, panning, and rotating are also performed in this window. |
| Drop Down Menus | Functions such as file management, edit controls, display options, user preferences, journal file management, window manipulation, and help are available in the pull-down menus. |
| Toolbars | This is a large selection of selectable icons that duplicate the functions found in the pull-down menus. Additionally, picking types, and mouse selection controls are found here. |
| Power Tools | The Power Tools contains the ITEM workflow, geometry repair power tools, meshing power tools, mesh/geometry comparison tool, defeaturing tool, assembly tool, and mesh quality power tools. |
| Command Line Workspace | The command line workspace contains both the cubit command,
error, history, and script windows. The command window is used
to enter cubit commands and view the output. The error window
is used to view cubit errors. The history window is used to view
recent commands. The optional script window is used for Python
programming. |
| Command Panels | Most Cubit commands are available in the command panels. The panel is organized topologically, by mode. |
| Properties Page | This is a list of properties of the selected geometry, mesh, boundary condition, or assembly. Some of the properties can also be edited from this window. |
| Model Tree | The model tree shows all geometric entities and their relationships, boundary conditions, boundary layers, and groups. |