Slot Surface Preparation with the Geometry Power
Tool
This page describes the slot surfaces diagnostic tool that is part of
Cubit's Geometry
Power Tool. The Slot Surfaces diagnostic is a new addition to the
geometry power tool for preparing slot surfaces in Electromagnetic (EM)
modeling. A slot surface is used to identify potential pathways where
EM radiation can potentially exit. This diagnostic will help manage slot
surfaces and prepare them for the application of boundary conditions and
analysis. This diagnostic utilizes Machine Learning (ML) to predict the
most likely slot surfaces.
Background
The Geometry
Power Tool in Cubit provides a series of diagnostic checks on your
model used to defeature or simplify a CAD model prior to meshing. Clicking
the Analyze button will perform the selected diagnostic tests and
display an expanding tree listing geometric entities that are identified
by each test. Once identified, suggested solutions can be easily previewed
and executed.
The Slot Surfaces diagnostics work best in conjunction with the machine
learning models. As such, to use this diagnostic the Load ML Models
button must first be selected using the procedure described in the page
Machine Learning with the Geometry Power
Tool.
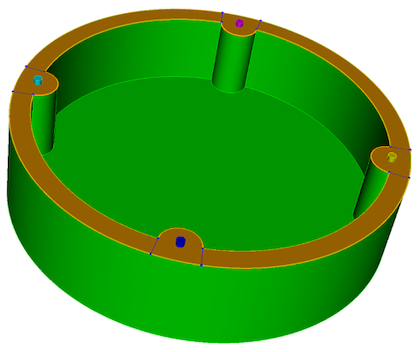
Figure 1. Example
volume showing slot surface highlighted. |
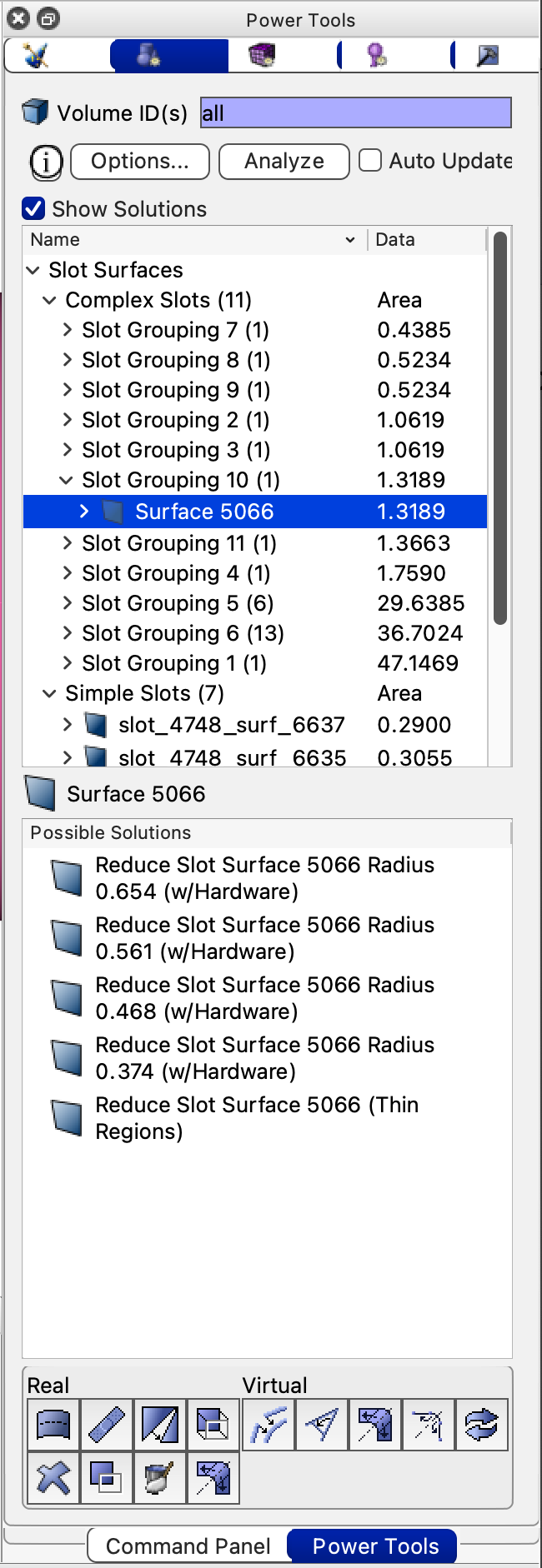
Figure 2. Slot
Surfaces diagnostic displayed with Solution window. |
Slot Surfaces
The Slot Surfaces diagnostic is only available when the ML Models have
been previously loaded in the Options panel. Once the ML models are loaded,
select the Slot Surfaces diagnostic from the list of diagnostic tools.
When this diagnostic is selected, the analyze button will identify all
surfaces that are identified as slots. The surfaces will be separated
into two groups: simple and complex.
- Simple Slots: Simple slots have four sides and can be used
directly for representing slots without further decomposition.
- Complex Slots: Complex slots can be comprised of groups
of adjacent surfaces or can be a single surface that may require additional
decomposition. For example, a gasket-type surface between two volumes
that may be held together with bolts or another type of fastener.
Each grouping of surfaces in the complex category can be expanded
and individual surfaces selected. Selecting a surface will display
potential reduce operations in the solution window.
Solutions Window
If the Show Solutions checkbox is selected, a list of potential
decomposition strategies will be listed in the solutions window. The decomposition
strategies will be variations of the reduce
surface slot command. Selecting a solution will preview where
cuts will occur and double-clicking will execute the cuts. If fasteners
are present, the ML tools should identify them and use them in the reduce
surface slot commands presented in the solutions window.
Right-Click Menu Options
The slot surfaces diagnostics provide many of the same visualization options
available with the other diagnostics. A few additional tools, useful for
shell modeling, are also provided and described here:
Export Slot Data
This option supports the setup of a Morph input deck and will execute the
command export
slot data. Morph is an external meshing tool developed at Sandia.
Morph supports slot surfaces for modeling EM, but requires named surfaces
and curves to identify the correct topology. When selected, a file browser
will appear where a filename can be specified. A text file will then be
written with the necessary information needed for Morph input for slot
surfaces.
List Slot Data
Executes the command export
slot data preview. Similar to the Export Slot Data... menu
option, rather than writing a text file, the information will be echoed
to the Cubit output window.
Reduce Slot Surface
Available when selecting a solution in the solutions window. The command
panel for reducing surface slots will appear. This panel provides options
to input the hardware and radius information, automatically populating
the necessary fields based on the slot geometry. Additionally, users have
the ability to specify grouping and naming options for the decomposed
slot surfaces.

